SOCKS is the protocol type supported by GOST. There are three versions of the SOCKS protocol: SOCKS4, SOCKS4A and SOCKS5.
SOCKS4
gost -L socks4://:1080
Standard SOCKS4 proxy service, compatible with SOCKS4A protocol.
SOCKS4A
gost -L socks4a://:1080
Standard SOCKS4A proxy service,
SOCKS4(A) currently supports only the CONNECT method and does not support the BIND method.
SOCKS5
gost -L socks5://:1080
SOCKS5 negotiated encryption
GOST supports the standard SOCKS5 protocol methods: no-auth (0x00) and user/pass (0x02), and extends two methods for data encryption: tls(0x80) and tls-auth(0x82).
Server side
gost -L=socks5://:1080
Client side
gost -L=:8080 -F=socks5://server_ip:1080?notls=true
If both ends are GOST SOCKS5 mode (as example above), the data transfer will be encrypted (using tls or tls-auth). Otherwise, use standard SOCKS5 for communication (no-auth or user/pass).
notls - (2.9.1+) You can disable negotiated encryption feature via this parameter, default value is false.
SOCKS5 UDP Relay
GOST SOCKS5 also supports UDP Relay, and supports TCP-over-UDP features.
No forward proxy
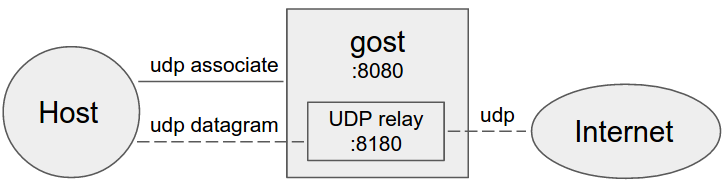
GOST acts as the standard SOCKS5 proxy for UDP relay.
Forward proxy
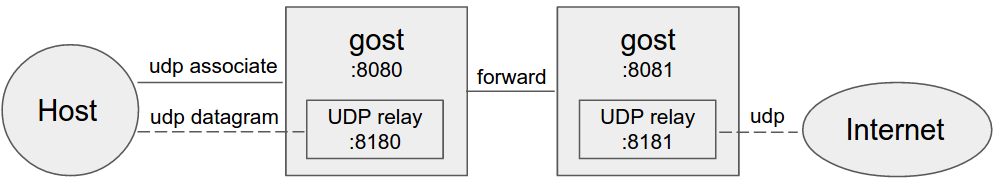
Multi-level forward proxy
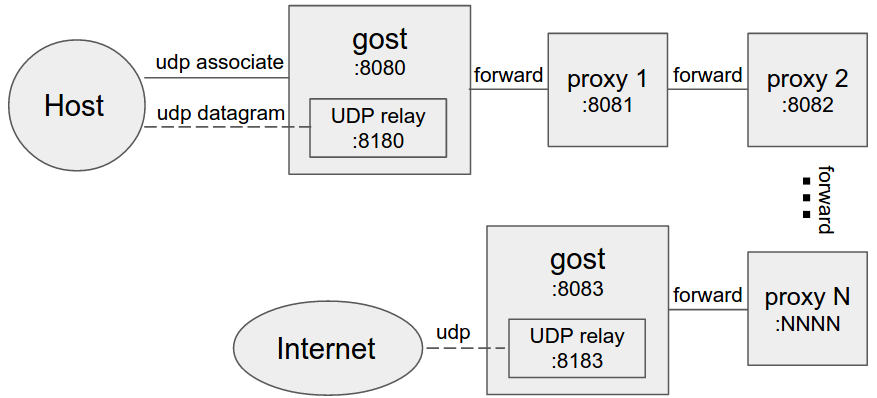
When forward proxies are set, GOST uses UDP-over-TCP to forward UDP data, proxy1 to proxyN can be any type.
If the BIND and UDP requests for SOCKS5 are to be forwarded, the end of the chain (the last -F parameter) must be the GOST SOCKS5 proxy.
The SOCKS protocol can also be used in combination with various transport types
SOCKS5 Over TLS
gost -L socks5+tls://:1080
SOCKS5 proxy service using TLS encryption.
SOCKS5 Over QUIC
gost -L socks5+quic://:1080